Percentage ratios: the yield on short deposits dropped below 19%

The yield on deposits for short periods, from three to six months, fell below 19% for the first time since August 2024, Izvestia found out. This happened after the Central Bank reduced the key rate to 20% — banks assume that in the near future the regulator will further soften the policy. Nevertheless, players are in no hurry to lower loan rates, although the largest banks have announced similar plans. The regulator's decision should support the economy, but during the summer several factors may come up at once in favor of price acceleration. Whether the Central Bank can abandon plans to lower the rate is in the Izvestia article.
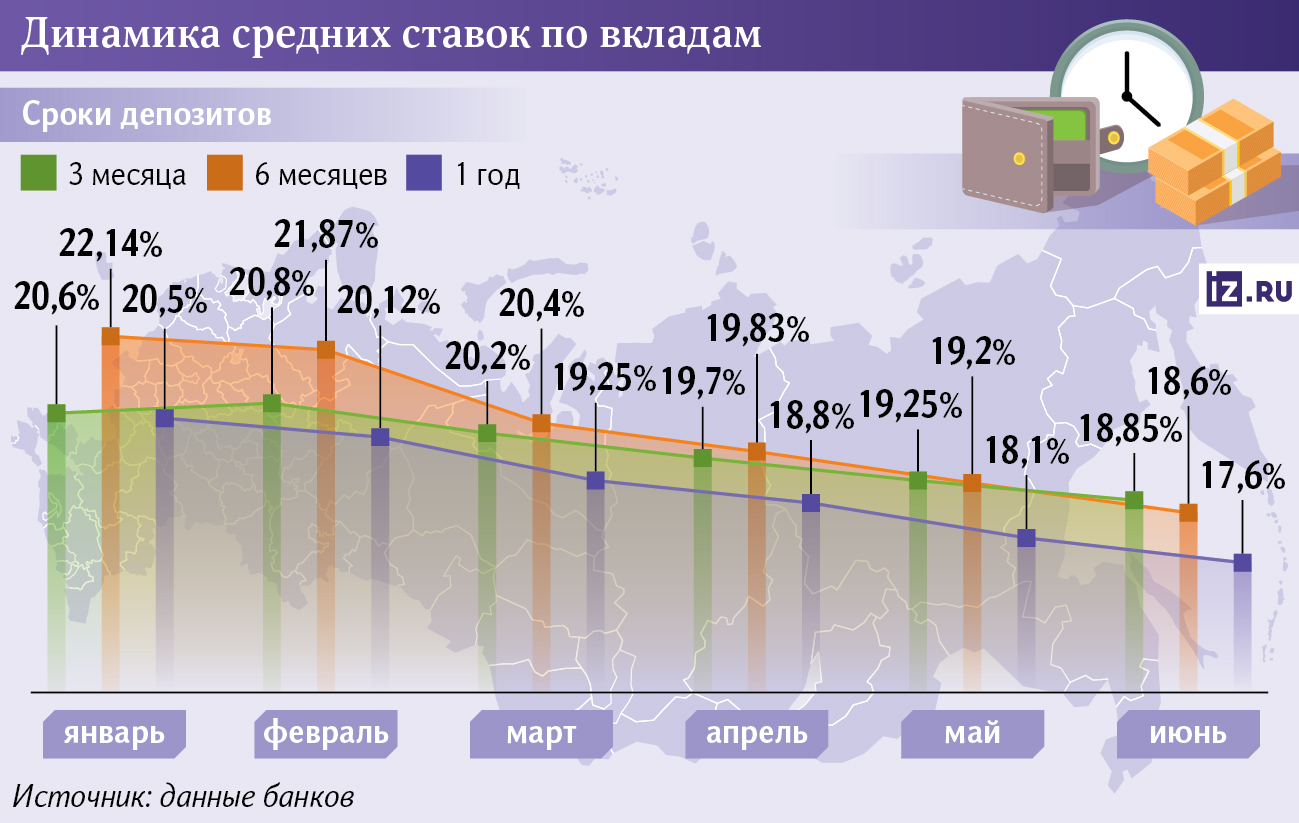
What are the current deposit rates?
The largest banks have reduced deposit rates for periods from three months to six months, dropping them below 19% for the first time since August 2024. Conditions worsened for more than half of the top 10 players, according to data from credit institutions' websites. For some market participants, the yield on short deposits is close to 17.5%.
At the same time, annual deposit rates decreased by 0.5 percentage points, to 17.6%, Izvestia found out. This means that banks expect further rate cuts by next June.
The Central Bank lowered the key rate by 1 percentage point, to 20%, at a meeting on June 6. The last time the Bank of Russia eased monetary policy was three years ago, in 2022. The main argument in favor of the regulator's decision now is the sharp slowdown in inflation in April. Price growth decreased to 6.2% year-on-year after 8.2% in the first quarter.
Despite the fact that deposit yields have already gone down, banks are in no hurry to lower loan rates. This is a fairly common situation after the easing of the PREP — for some time, market participants continue to issue loans with the same value, while deposits become less profitable.
— There will be no sharp reduction in retail loan rates. Even with a key interest rate of 20%, the cost of loans remains extra—high, and a full-fledged "credit renaissance" is still far away, according to the VTB press service.
Banks issue loans for the money they attract through deposits, and their profitability directly affects the cost of loans. However, now the market needs to recapture the funding they received at interest rates above 19%. To lower loan rates, they need to collect more funds from Russians for new deposits, and this takes time.
Nevertheless, some players promise to reduce the cost of loans in the near future. For example, immediately after the Central Bank meeting, Sber announced plans to lower rates on market mortgages and consumer loans from June 10. In the press service of the Bank "Dom.The Russian Federation also announced plans to reduce consumer loan rates by 2 percentage points in the coming weeks.
Some players have included a key reduction in the cost of products in advance — for example, MTS Bank lowered deposit rates last Tuesday. Izvestia has sent a request to other major credit organizations to improve loan conditions.
How will lower deposit rates affect the economy
The dynamics of deposit rates directly reflects market expectations regarding further decisions of the Central Bank on the key issue. Investors are confident in the transition of the regulator to a cycle of easing the PREP, noted in the "Digital Broker". Nevertheless, players are not convinced about a further rate cut at the July 25 meeting, otherwise deposit yields would have dropped even more, Finam added.
Due to the rate cut, the Moscow Exchange Index may reach 3,200 points by the end of 2025, which is almost 20% more than it is now, said Andrey Smirnov, an expert on the stock market at BCS World Investments. Due to lower deposit yields, huge amounts of money may enter the market in the future, which will support the country's economy, Finam noted.
On Friday, the Central Bank lowered the rate contrary to the consensus forecast of the market, which expected a softening of the PREP only in the second half of the year. The regulator's actions are essentially a compromise between the fight against inflation and the desire to increase GDP. The Bank of Russia reported a gradual slowdown in the Russian economy, but experts spoke bluntly about the risks of its "hypothermia."
Of course, the growth of investment activity will support the country's economy, but in this situation it is important to prevent a reversal of the trend towards a slowdown in price growth. According to the head of the Central Bank, Elvira Nabiullina, inflation is even more detrimental to the economy and severely affects the well-being of ordinary people.
Will prices continue to rise in the second half of 2025
The dynamics of the monetary policy of the Russian Federation shows that with a decrease in overall inflation in the country, the cost of essential goods may continue to rise, said Olga Belenkaya, head of the Macroeconomic Analysis Department at Finam. According to her, the cost of products for ordinary Russians depends not so much on the rate as on supply factors, such as the harvest in the Russian Federation, duties and the cost of transporting goods.
Even now, inflation is mainly slowing down due to lower prices for non-food products, such as cars, smartphones, and others, Finam said. Imported products that are bought in foreign currency are getting cheaper against the background of the ruble's growth. Since the beginning of the year, it has grown by almost a third and reached the level of 79 per dollar. At the same time, basic goods, food and services are rapidly becoming more expensive.
The growth rate of prices for goods consumed by Russians every day makes ordinary people expect further acceleration of inflation, Olga Belenkaya said. This factor itself affects the price increase, because people try to buy for the future, which only pushes them to consume.
— In general, the future reduction of loan rates should support producers. If their expenses decrease, all categories of goods will be able to fall in price," said Natalia Milchakova, a leading analyst at Freedom Finance Global.
At the same time, prerequisites for an additional price acceleration may appear before the end of the summer. Starting in July, utility tariffs will be indexed by an average of almost 12%, Finam recalled. In addition, due to the unstable weather this spring, there are risks of a decrease in the harvest, which can also accelerate the prices of vegetables and fruits.
The fight against inflation is not over yet, because the trend towards a slowdown in price growth may reverse. This does not mean that the Central Bank may go back to key growth, but it should be borne in mind that the regulator's forecast for a long period of tight PREP is still relevant.
Переведено сервисом «Яндекс Переводчик»







