- Статьи
- Science and technology
- Sweep out of orbit: the first reusable space garbage collector is being created in Russia
Sweep out of orbit: the first reusable space garbage collector is being created in Russia
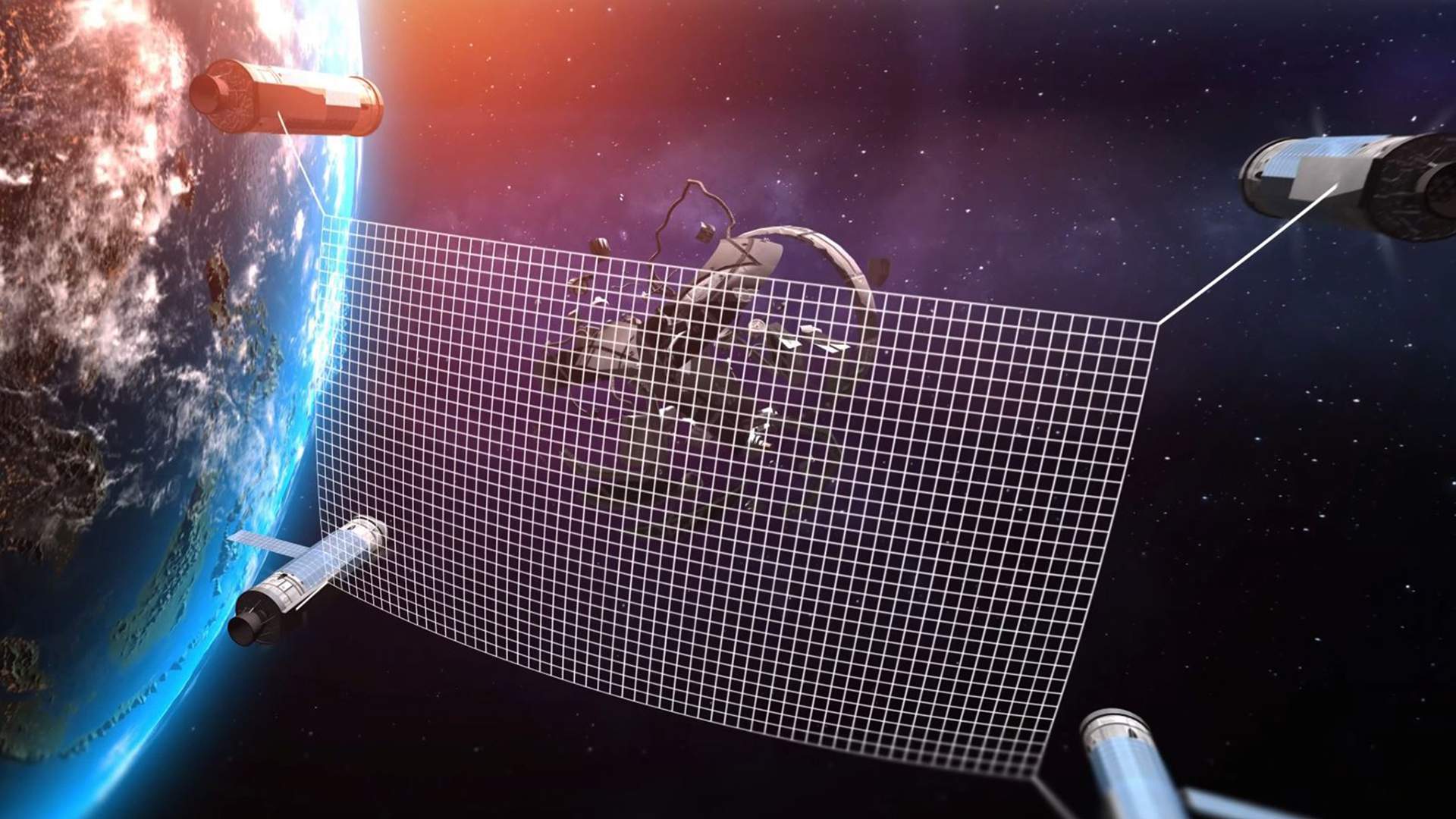
Scientists are creating the first Russian space transporter satellite to clear space debris from orbit. There are only eight such devices in the world. The uniqueness of the domestic development lies in the possibility of reusable use of the garbage collector with the option of returning one of the modules to Earth. The authors are preparing for a test launch in 2025, and experts believe that the project still looks too ambitious and expensive for early implementation.
What is a space transporter
Russia has developed a test sample of the first reusable device for collecting, transporting and disposing of debris in orbit. This was reported to Izvestia by the press service of the National Technology Initiative (NTI).. It is assumed that it will solve the problem of space debris — the device is able to do this point-by-point and safely without the risk of creating new fragments. At the same time, the transporter is capable of moving any objects in space, for example, moving satellites between orbits, extending their service life.
The technology is capable of returning satellites to Earth for repair and reuse, and is also capable of relocating any objects depending on the tasks, Ali Al-Zubeidi, head of the VT Empire development company, told Izvestia. At the same time, the device itself is able to operate without returning to Earth.
— The space transporter is actually a satellite for cleaning the orbit from space debris. At the moment, there are only eight such vehicles worldwide, but none of them can be returned to Earth for maintenance and re-operation. The uniqueness of our product is that the garbage collector is reusable. We are currently preparing for the first test launch of the spacecraft into space. The project is at an early stage of development, but there are already achievements: for example, we became finalists for the prestigious GSEA award and were awarded by Moscow Mayor Sergei Sobyanin," he said.According to the co-founder of the project, Ahmed Al-Zubeidi, the technology will solve the problem of space debris in orbit using a device to clear space of outdated artificial Earth satellites and their debris. The problem is real, because satellites, the ISS and future missions are already threatened by more than 8 thousand tons of space debris, he added.
The conveyor collects space debris and debris thanks to a modular system and a grid capable of withstanding ultra-high temperatures. When debris is detected , the modules are undocked and debris enters the network. One of the modules returns to Earth, while the debris is burned in the atmosphere, the expert specified.
How the experts evaluated the novelty
The development of such products is more relevant now than ever, said Andrey Galinovsky, a leading researcher at the NTI Center for Digital Materials Science: New Materials and Substances at the Bauman Moscow State Technical University.
— The project involves not just a satellite, but a sufficiently maneuverable conveyor system with its own propulsion system, control systems, separation of modules, robotic object capture devices, etc. This requires at least serious cooperation. In addition, the presence of satellites in Russian laboratories that have been in orbit for a long time will help to assess the complex impact of negative factors of outer space on nodes, instruments and materials," the expert emphasized.
However, speaking generally about the task of cleaning orbits from debris, everything depends on financing, said Andrey Novikov, associate professor, Deputy Dean of the Faculty of Special Engineering at Bauman Moscow State Technical University. As long as launches are possible and orbits are relatively free, it is unlikely that substantial money will be allocated for this.
— The problem of space debris is already becoming acute. Today, when launching manned expeditions, a window is selected separately in which the risk of collision with debris is minimal. Space agencies have a map of debris objects larger than 10 cm. Large satellites, spaceships, and orbital stations can dodge it, but this is a half-measure. It's time to start "cleaning" the orbit. And now there are a number of ideas and developments dedicated to this. This should be a global task, and the space agencies of the largest countries should unite and solve the problem together," he said.
At the same time, it is unclear to the specialist what will ensure reusability, how garbage will be removed and where fuel reserves will be replenished.
— And we no longer have such technologies for the return of satellites entirely. When there was the Energia-Buran or Space Shuttle system, yes, it was possible, there was a large payload bay. But now returning objects to Earth is an extremely difficult task due to the enormous thermal loads. And reusable devices are very expensive. In 2011, the last year of the shuttle's operation, one of its expeditions cost NASA more than $800 million,— added Andrey Novikov.
The idea itself repeats the technology of the American company — fishing with a net. But in domestic development, modules must maneuver around the object, it is much more difficult, said the CEO of the company "Sputnix", expert of the NTI working group "Aeronet" Vladislav Ivanenko.
— The main difficulty in capturing space debris is that it moves at a tremendous speed. Such operations are almost always associated with the risk of damage to the device. In this regard, it remains unclear how reusable the system will be and whether the increased costs of its development and operation will be justified. Perhaps the use of disposable systems will be more economically beneficial," said an IT expert and senior lecturer at the Department of Esports at the University's Faculty of Gaming Industry and Esports."Synergy" Daniil Arzhakov.
At the same time, he noted that the development is unique for Russia, but it also highlights the lack of experience among domestic specialists in this field, which may increase the risks during the implementation of the project.
Переведено сервисом «Яндекс Переводчик»





