- Статьи
- Internet and technology
- "There are fewer countries with digital sovereignty than countries with nuclear weapons"
"There are fewer countries with digital sovereignty than countries with nuclear weapons"

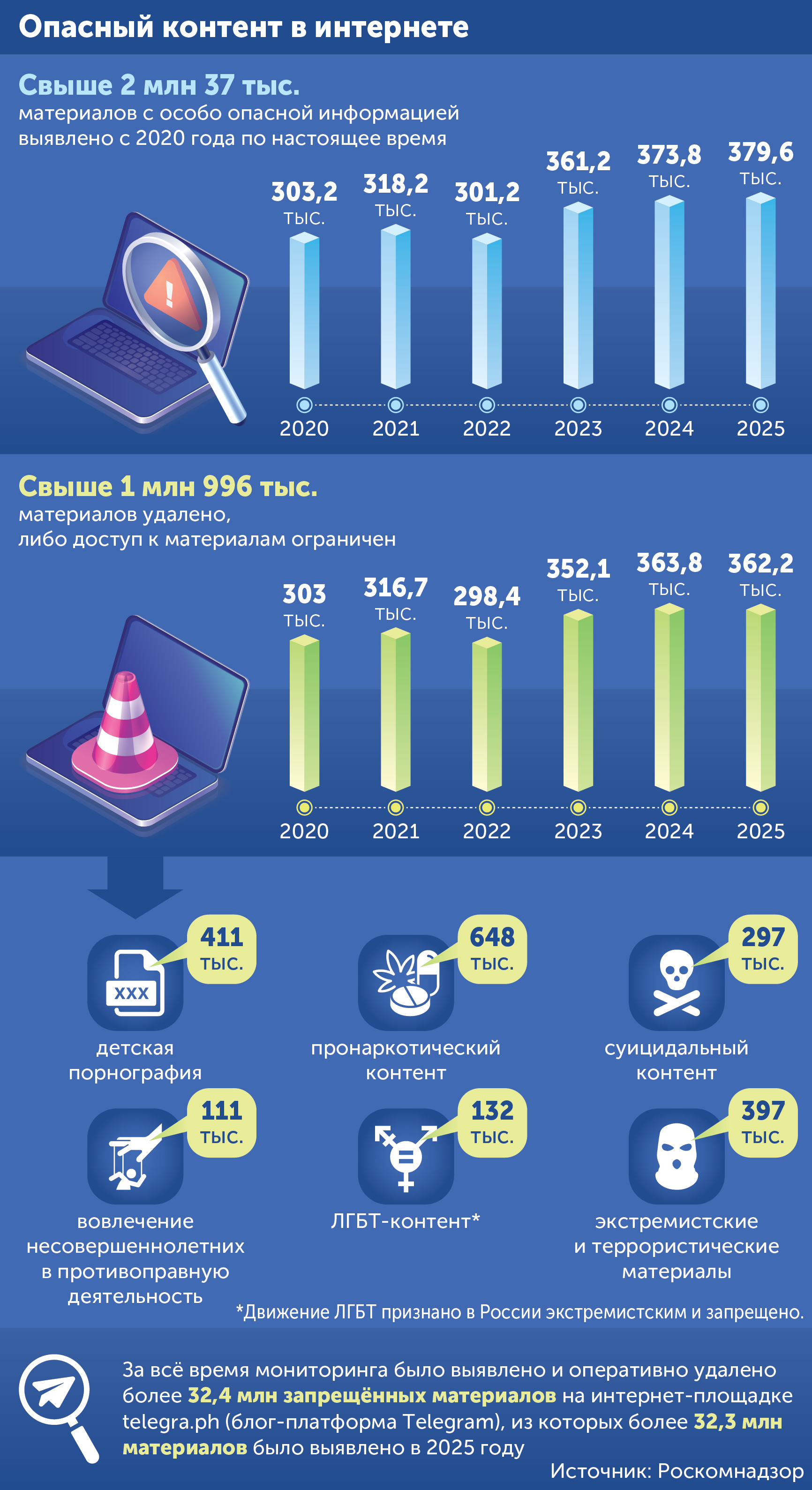
In the first half of 2025, according to the requirements of Roskomnadzor, more than 425 thousand units of illegal Internet content containing child pornography, drug propaganda, extremist materials and fakes were removed. In an interview with Izvestia, the head of the service, Andrey Lipov, spoke about the main threats in the information sphere, digital sovereignty, and personal data protection, and also assessed the effect of limiting the functionality of foreign messengers in the fight against fraud.
"Threats in the information sphere"
— Today we live in a world where digital reality has become an integral part of our lives. Unfortunately, this space is fraught with many dangers, especially for the most vulnerable — for our children. What threats on the Web do you consider to be the most serious and how does Roskomnadzor protect citizens from them?
— The Internet environment today gives people not only a huge number of opportunities, but also, due to the way it is organized, carries very serious dangers. They are more complicated than in ordinary life. Crimes on the Internet are more difficult to detect, more difficult to prevent, more difficult to collect evidence, more difficult to find and punish the perpetrator. Now every agency that ensures the safety of our citizens is constantly fighting these threats on the Internet. We work in constant contact with colleagues. Almost all decisions about taking action on the Internet come to us for implementation. We really see that the main crimes on the Internet are committed against the most vulnerable — against the elderly and children. And these crimes are committed in the vast majority of cases using foreign Internet applications.
Of course, the main task of Roskomnadzor is to protect our citizens in the information environment. First of all, we are talking about protecting children and our future. For them, any threats are scarier than for adults. Propaganda and distribution of drugs, child pornography, and suicidal tendencies are absolute, unconditional evils. And these are just the most common crimes. About ten years ago, the country was shaken by a series of tragic cases when the activities of so-called death groups on social networks led to the deaths of children. Criminals moved from distributing dangerous content to direct contact with children. The curators of suicidal communities, most of whom were from Ukraine, conducted a real special operation against our children, provoking them to perform tasks in a playful manner, where suicide became the final stage.
In order to quickly close these "death groups", the agency has established a separate monitoring of suicidal content on the Internet. In total, in order to bring down the wave of Internet suicide, we stopped the distribution of 493,000 such materials, including 91,000 through citizen appeals. Amendments were made to the legislation, which tightened criminal liability for the creation of such communities.
Starting with their involvement in "death groups" through social media, the criminals continued to improve their methods and skills. They are constantly looking for new ways to identify victims, influence them, and commit crimes. And now phone and online fraud has become a real gold mine for them. Using their accumulated experience, they cheat, extort money, using people's gullibility and fear, and draw them into committing extremist actions. Since the beginning of the special military operation, aggression against Russians has become a system — open, large-scale and coordinated by foreign intelligence services. And all the same criminal call centers are operating from the territory of Ukraine.
And here we face a very serious problem: foreign messengers, foreign social networks, which are the main place of commission of these crimes, do not respond to our legitimate demands for their suppression, identification and punishment of criminals. They, in fact, refuse to protect their users from Russia, actually supporting aggression against Russians in their services.
We continue to look for ways to protect ourselves here. We managed to learn how to selectively block the functions used by scammers, in particular voice calls in messengers. We act like jewelers, surgically — we try to block channels for intruders, without blocking access to important information and services, so that most of our users do not experience inconvenience. Of course, the fraud has not been completely stopped, not all channels are blocked. But experts continue to work on this, improving methods and tools of counteraction.
— Give examples of how much illegal content can be blocked or deleted from foreign digital platforms.
— The situation with the removal of illegal content from foreign digital platforms, as mentioned above, remains difficult. We see that a significant part of the dangerous information continues to be available on them.
For example, since the beginning of this year, more than 210.6 thousand materials with illegal content have been deleted from Telegram. But there are still more than 155.8 thousand dangerous publications available there. The situation on YouTube is similar: about 4.8 thousand pieces of content have been deleted, but another 67.7 thousand materials are available. It's all the same information about drugs, child pornography, LGBT* materials, materials from extremist and terrorist organizations.
A fresh example. Over the past two months, our systems have identified several million drug-related new materials on a popular foreign blogging platform. According to our requirements, this most dangerous array of content was promptly deleted. But this is an ongoing job that actually needs to be done by the platforms themselves and proactively.
I would like to emphasize that the government is conducting systematic and long-term work to bring popular foreign digital services into compliance with Russian legislation. The law "on landing" created all the conditions for their work in Russia. I personally held repeated meetings with the management of these companies on the VKS, explaining and discussing the basic rules of work in our country. But all these Internet giants, observing exactly the same rules in other countries, removed their offices from our country or did not open them, and chose to ignore our legislation.
We regularly draw up reports on administrative offenses, and the courts impose appropriate fines. Since 2021, the total amount of fines imposed on platforms for failure to delete prohibited information has exceeded 35.4 billion rubles. These are serious amounts, but, unfortunately, fines do not always give the desired result. Fines always follow an offense when the harm has already been done. And often irreparable harm. Therefore, our task is to build up our own, full—fledged digital sovereignty, in which our citizens could use their usual opportunities without experiencing the threats from which they are currently not immune on foreign Internet platforms.
— The spread of fraud and the refusal to comply with Russian laws in the fight against crime have led to restrictions on calls to WhatsApp and Telegram. Has the effect of this measure already been shown?
— The effect of call restrictions on WhatsApp and Telegram was immediately apparent. We managed to selectively limit the functionality that scammers mainly use, because for them voice contact with the victim is fundamentally important. After that, the scammers tried to return to regular telephone communication, but they no longer receive calls with a number substitution. This was made possible by the Antifraud system, which Roskomnadzor launched in December 2022. The system verifies from 400 million to 600 million calls per day, detects and blocks from 1 million to 2 million calls with signs of number substitution. 1108 telecom operators are connected to the system, which makes it possible to verify all incoming calls from them, regardless of fraudsters' attempts to hide their real number. Our "Anti-fraud" works in real time, ensuring the prompt exchange of information between operators and the immediate blocking of unconfirmed calls by operators. The system checks whether the telecom operator who owns the caller's number has initiated the call. If not, the call is blocked. It's fast and efficient.
Nevertheless, the scammers do not give up and now use Russian SIM cards when calling from roaming. But here, too, we have a solution: we are currently checking the work of the operators and, based on the data from our system, we require them to clear their databases of fake users.
In addition, we have started working with operators to inform our platforms, including messengers, about roaming SIM cards online. For accounts registered on such SIM cards, platforms could impose partial, temporary restrictions. At the same time, it is necessary to think over a system of exceptions for respectable Russian citizens traveling abroad on vacation or for work.
It is logical that for calls from abroad via messengers from accounts registered with foreign SIM cards, the messengers themselves imposed call restrictions by default, with the ability for users to independently make exceptions for their specific number lists. Our telecom operators should do the same when making calls from foreign numbers over regular telephone networks. Of course, with unconditional respect for the rights of our citizens to receive communication services. All these proposals have been sent to the Government for inclusion in the second package of anti-fraud measures.
In addition, additional adjustments are required to work with SIM cards and our digital platforms. Often, people working through these platforms use other people's SIM cards (up to 60%), which makes it difficult for the platforms themselves to detect fraud. We are currently discussing with domestic platforms the organization of online verification of the ownership of SIM cards used to interact with them through our systems.
By the way, the above examples, and they are not the only ones, of the participation of our state and state systems in ensuring the safety of their citizens when working with digital platforms, are apparently unique for most countries of the world. This is the result of our constant, of course, difficult dialogue with the business, and our joint search for effective organizational and technological solutions. We strive to create a sovereign and secure, full-fledged digital environment in Russia, where the state not only acts as a legislator and demanding executive authority, but also assumes responsibility, costs and coordination to create a common information security infrastructure with business, which underlies the country's digital sovereignty.
"There are only a few countries with digital sovereignty"
— In Russia, people often talk about sovereignty in the information space. How do you understand it and why should it be defended?
— Digital sovereignty, in general, can be simply defined. This is when a country has all the modern Internet services, software, computing power, networks and communication facilities that citizens, businesses, and the state need, which are independent of foreign influence and are in constant development. Further details can be provided. Using these Internet services, which make up the country's digital ecosystem, should be comfortable, safe and profitable. At the same time, the digital ecosystem must be technologically reliable and sustainable, its data must be protected and integrated, and its services must be accessible to users across the country.
The most important sign of digital sovereignty is the ability of the national digital ecosystem to continue to work just as effectively even in the face of external attempts to disconnect us from the foreign Internet or attempts to disrupt our digital services within the country. Digital sovereignty is also the ability to defend oneself.
In other words, there are two main directions for the development of digital sovereignty — the digital ecosystem of services and the digital security infrastructure on which this ecosystem confidently operates.
There are only a few countries with such full—fledged digital sovereignty, even fewer than those with nuclear weapons. Russia, the United States, and China are just a few capable of creating and maintaining digital sovereignty of this level.
— What should be the most important elements of national digital sovereignty?
— We have the most important elements of digital sovereignty. These are primarily Russian search engines, social networks, an app store, video platforms, and a messenger. They give us information independence. Plus, the security of information and the stability of its transmission are guaranteed to us by our automated Internet security system and our own traffic routing systems in Runet.
We also have a huge range of Russian Internet services that are part of the national digital ecosystem: marketplaces, maps with navigation, banking, delivery and taxi services, HR services, online education, online cinemas, music services, video hosting, electronic media, services and portals for citizens and businesses to interact with the government. But at the same time, I would like to draw your attention to the fact that without the national RuStore app store, it would be impossible to guarantee the availability and relevance of versions of all listed Russian services.
The national digital security infrastructure, which ensures widespread and permanent availability, security, reliability and stability of Internet services, includes the country's communications network (including lines, equipment, facilities and communications facilities), data centers and hosting, Geo-IP, systems for identifying and protecting against network vulnerabilities and attacks. This includes DDoS attacks, a call blocking system with number substitution and the already mentioned automated Internet security system, national traffic addressing and routing servers.
The emergence of the national messenger MAX has become an extremely necessary step in strengthening digital sovereignty. Its development was carried out with the priority of ensuring the comfort and safety of users. A critical positive difference of MAX is the targeted and effective fight against fraudsters. The integrated systems and security services of the national messenger have already blocked more than 70 thousand SIM cards from which criminals called our citizens. The messenger is currently actively developing, providing users with new convenient services for the safe receipt of public services, education, news and communication.
Digital sovereignty is also the application of a wide range of domestic software, primarily in our industry. The priority of use in computing should be the national operating system. An important link for digital services is the national mobile operating system. Unlike in the USA and China, mobile phones with our national mobile operating system are not yet being mass-produced. This is a serious task that needs to be solved. As well as continue to actively develop the national low-orbit satellite communications system, including those that ensure the operation of conventional mobile phones.
The dominance of Russian content in our digital services cannot but be attributed to digital sovereignty. Fortunately, in recent years, our video hosting sites, social networks, and online cinemas have been filled with high-quality domestic products of a wide variety of formats and themes.
Digital sovereignty is ensured not only by Russian companies and government efforts that create a national digital ecosystem of Internet services and digital security infrastructure, but also by Russian users — citizens of our country. An important part of digital sovereignty is understanding risks, following certain rules, and developing skills to use Internet services safely. As an example: The fact that you can't tell anyone your password under any circumstances should become as natural an internal taboo as the prohibition against running a red light across a highway with a rushing stream of cars. The common task of the state and business is not only to protect, but also to continuously improve the digital literacy of our citizens, primarily children and the elderly.
According to opinion polls conducted in recent years, it is clear that the majority of Russians realize and support the need for digital sovereignty. The independence and independence of the state in the digital environment is perceived as a necessary continuation of national security. And I must say that now citizens perceive Roskomnadzor as an agency that protects their interests, the interests of society and the country, which means they understand the complexity of the challenges we are responding to, and they understand the need for our work.
— How does Roskomnadzor help citizens who have become victims of fraud, and what support mechanisms exist for those who face violations of their rights in the digital environment?
— At some point, we realized that citizens are often left alone when they have to defend their interests in the digital environment, challenge injustice, defend themselves in court, and collect documents and evidence. In 2021, on our initiative, the Center for Legal Assistance to Citizens in the Digital Environment was established, a structural unit of the FSUE Main Radio Frequency Center. His mission is simple, but very important: to help our citizens, who have suffered from digital offenses during the use of modern Internet technologies, for free. For example, due to leaks of the same personal data, as a result of which microloans and loans are taken on a person without his knowledge. Since 2022, we have opened regional branches of the center in the North-Western, Volga and Siberian Federal Districts. We also work for applicants from other regions — we help remotely.
— How does it work in practice?
— The center's specialists provide free legal assistance: they prepare claims, file lawsuits, and represent citizens in courts. The main requests are the protection of personal data, the fight against fraud, and the restoration of honor and dignity after the publication of fakes. In the first half of 2025, we received 4.7 thousand requests, which is a quarter more than a year earlier. At the same time, more than half of the requests are directly related to crimes in messengers: people lose money and property.
Recently, we were contacted by an elderly Muscovite who became a victim of fraud, who was "processed" through WhatsApp. Under the guise of intelligence officers, the attackers convinced the pensioner to apply for loans and sell her only apartment in order to "protect funds from terrorists." The woman transferred all the money to a "secure account", and then the deception was revealed. Fortunately, the lawyers helped to invalidate the purchase and sale transaction - the court of first instance has already satisfied the claim.
We actively work not only with courts, but also with educational projects. We conduct lectures in schools and universities, and cooperate with the children's rights commissioners in 38 regions. It is important that today's schoolchildren are able to distinguish fake from the truth, and pensioners are not afraid to use online public services and other useful Russian digital services.
— I just wanted to ask about the stability of the services. Subscribers have been constantly complaining about mobile and Internet failures lately. And admittedly, high-quality voice communication is not available everywhere in Russia. Why is it sometimes impossible to get through to a regular number even in the center of Moscow, and have such cases become more frequent recently?
— In my opinion, everything is clear to everyone here. Nothing is more important than the life and health of our people. And it is not necessary to create HYPE from each such case of disconnection of the mobile Internet. The media should just calmly inform that work is underway to protect the population. Enemy drones that pose a threat can use radiation and data transmission from mobile base stations for navigation, guidance. This is a necessary security measure, and it will always be applied by the authorities based on the operational situation "here and now".
I would like to add that we need to adjust the strategy of regional development of communication networks, switch to more flexibly operating base stations, domestic developments with different antenna characteristics are needed, and operationally, citizens should focus on connecting via dedicated communication lines, including via Wi-Fi. For telecom operators, it is important to expand urban networks with Wi—Fi coverage as actively as possible.
About the quality of the connection. We need to return to rationing requirements. They were canceled at the time — they hoped that the vendor would not deliver anything bad. But now we need to bring back these requirements, as well as the requirements for the reliability and stability of our networks, lines, facilities and communications facilities.
— Let's just talk about the sustainability of the Runet, I think that the closest public attention of all Roskomnadzor's projects was to the implementation of the law on the "sovereign Internet". As far as we know, you were at the origin of its development back when you worked in the presidential administration.
— Back in 2014, the tasks of strengthening the security of the information space and ensuring digital sovereignty were set. The decisions were made at a meeting of the Security Council on October 1, 2014, which was held following the results of exercises and research simulating various threats, including the threat of destabilization of the Internet in our country.
Despite the stability of the Russian communications network, its good connectivity and the presence of many cross-border lines, dependence remained on foreign Internet management infrastructure located in the United States and other countries. In this regard, work has begun on creating its own replacement infrastructure, and in 2019, the law on the "sovereign Internet" was already adopted. Its main goal is precisely to ensure the security of our information space, to ensure the uninterrupted operation of Russian digital services, and to be able to promptly identify and respond to new network and information threats.
As part of this work, a number of systems have been created, including those already mentioned, which are used by almost all of our telecom operators and our owners of autonomous Internet systems. For example, this year alone, the number of daily requests to the established national addressing system on the Internet has exceeded the impressive mark of 40 billion.
"We identify up to 98% of illegal information that is particularly dangerous for citizens"
— Over the past five years, Roskomnadzor has significantly increased its powers and capabilities in the information sphere. What goals and objectives have you set for yourself? And what did it take to solve them?
— Five years ago, continuing to solve the task of ensuring digital sovereignty, our team began by identifying the key projects of the department for the medium term. To implement them, it was necessary to modernize, implement project management and objective, operational control over the achievement of goals and indicators.
We selected 11 of the most important projects from a variety of projects, combined them into a single plan, synchronized the results and set a deadline for completion of work — a few months before the 2024 elections, leaving a reserve of time for the final adjustment of the systems. Our task was extremely simple: to exclude any possibility of illegal external influence on the electoral process in Russia.
Based on the number of key points (the number of full—time working months), they came up with a name - the "20-step Plan". It includes projects in all areas of Roskomnadzor's activities: three projects in the field of information, six in the field of communications, and two in the field of personal data. Regular project committees were organized for each of them under the leadership of the deputy heads of Roskomnadzor, at whose meetings the current results were analyzed and problems were promptly solved. In total, 12 new systems have been created and implemented during this time, as well as more than five existing ones have been upgraded. My colleagues talked about this in detail in their summer interviews with your publication.
All our systems are managed by the Center for Monitoring and Management of Public Communications Networks (CMU), established as part of an enterprise subordinate to Roskomnadzor in accordance with the law on the "sovereign Internet". The task of our structure is to identify and neutralize network threats. In accordance with the law, we conduct joint exercises every year with colleagues from other departments. During them, new threats are identified and the effectiveness of the created systems is checked. In fact, the CMU today is the center for operational management of the country's digital security infrastructure, a key subject of our digital sovereignty, protecting the country from network and information threats around the clock.
CMU has created a number of systems that now make it possible to effectively combat cybercrimes and counteract the anonymity and impunity of fraudsters. In April and May 2025 alone, operators blocked 5.3 million SIM cards, the owners of which did not provide reliable information about themselves, while an average of 1.2 million calls with number substitution are blocked per day. All checks are carried out through our systems.
Another of our developments is the National DDoS Counteraction System, which since its launch has successfully repelled more than 16,000 attacks from abroad (5.4 thousand in the first half of this year) aimed at Russian information resources, systems and communication networks. Today, more than 1.2 thousand organizations are connected to it, including large public and private structures, telecommunications companies, banks and operators of critical information infrastructure. The number of participants in the system continues to grow.
Technological changes have also affected the sphere of personal data protection. The Agency has implemented an automated system for monitoring the rights of personal data subjects, which monitors the legality of data collection on Internet resources. We have significantly reduced the amount of manual labor during these inspections, increasing their accuracy, speed and coverage. Thanks to the use of the system, labor costs were reduced by 75-80%, and the coverage of the resources checked annually increased many times — from 6 thousand in manual mode to more than 50 thousand in automatic mode. Thanks to this system, we have multiplied the number of detected and eliminated violations in the processing of personal data of our citizens.
— And how does Roskomnadzor's systems work in the field of mass communications?
— We have implemented a number of new information system modules in this area. They are responsible for searching for illegal content on Internet sites and in social networks, analyzing text, audio and visual information. Various neural network technologies are used here, demonstrating good results in automatic analysis, including images and videos.
We have managed to achieve high accuracy in detecting prohibited information by systems for most types of content. In relation to the most dangerous types of such information for society, the accuracy reaches 98%. At the start of the systems, this figure reached only 10%. This is a difficult, in many ways unique job that requires constant effort.
Most of the prohibited materials are removed, but access to many dangerous resources has to be restricted technically. The automated security system analyzes network traffic and currently restricts access to more than 1 million prohibited information resources.
The introduction of artificial intelligence technologies has reduced the detection time of prohibited information from the moment it appeared online to an average of six hours (compared to 48 hours in 2020). This is a worthy result, given the huge and ever-growing amount of information on the Internet, but we strive for even higher results.
On average, our automated system filters out and downloads about half a million materials with the appropriate tags every day. After analyzing with the help of neural networks, there are about 2 thousand materials left, on which decisions are already being made. Without new technologies, such an ever-growing amount of information is simply impossible to process.
— Do you use the expertise of third-party organizations to develop and improve your systems?
— Yes, you can't do without contractors. Of course, these are domestic proven companies. It would be strange to say that we have all the resources and expertise available. To create the most complex information systems of federal importance, we hold competitions, attract contractors, and carry out the operation on our own.
Among such projects, I would like to highlight the creation of a unified register of online advertising. The system is perhaps unique for the whole world — it is the first online advertising registry that allows anyone who sees it online to check its registration online. The creation of the registry was preceded by extensive consulting and analytical work with major advertisers and advertising distributors. This is a highly loaded system that requires significant computing power.
Today, the registry contains information on more than 68 billion advertisements, statistics on trillions of ad impressions on various platforms (websites, social networks, messengers, etc. — only 1.5 million sites). The system takes into account the advertising of 1.29 million advertisers annually. Last year, their advertising budget, reflected in the system, amounted to 858.6 billion rubles.
Thanks to this registry, we were able to introduce mandatory social advertising. Now 5% of online ad impressions are aimed at attracting people's attention to useful and non-commercial projects that talk about our traditional Russian values. Previously, it was extremely difficult for such projects to reach Internet users. Plus, we see how the Internet economy is developing by region and by industry. This analysis could not have been obtained before the system was created. Now we always have this information at hand — online.
— Roskomnadzor is considered a service that also brings economic benefits to the country.
— Nevertheless, the main task of Roskomnadzor is the safety of citizens and society on the Internet, first of all we protect people. But at the same time, we are making our positive contribution to the formation of the country's budget. The mentioned advertising accounting system has become a new source of budget revenue. Starting this year, a three percent fee has been introduced for the distribution of online advertising. According to preliminary calculations, already at the first accrual, for the second quarter of 2025, the fee replenished the treasury by almost 4 billion rubles. We expect to receive at least 12-15 billion rubles annually. In addition to the advertising fee, the agency also carries out a fee for the use of the radio frequency spectrum.
In total, according to all indicators, we are a surplus agency for the state. In absolute terms: in 2024, the department's revenues amounted to 43.2 billion rubles, and in 2025 we expect 46 billion rubles.
— The threats you mentioned earlier are changing by the second. New ones are appearing, existing ones are growing. How does this affect your work?
— In order to identify new types of threats, in addition to the CMU, we have created a Scientific and Technical Center that constantly conducts research. This allows us to predict future challenges by analyzing their possible consequences.
Scientific and technical councils have been organized at the NTC for each of the areas of Roskomnadzor's activities. The councils included leading representatives of the industry, the scientific community, and government authorities. This format provides us with the necessary horizons in expert support.
The result of this work is both new technical solutions and information systems, as well as proposals for making necessary changes to legislation. Over the past few years, the agency's number of powers has grown from 80 to 250. And first of all, we owe the new powers, of course, to the growth of threats in the digital environment.
"AI is the most powerful leap in quality in working with information"
— Now, any large or small company's task is to optimize all processes using AI as much as possible. How to regulate actively developing information access systems using artificial intelligence?
— Now a new model of relationships is being formed within the Network between information resources and AI systems on the one hand and consumers and AI systems on the other. AI is the subject of constant research in recent years of our Scientific and Technical Center.
In the broadest sense of the word, AI, which we all encounter on the Internet now, is such super—smart recommendation systems. In advertising, AI recommends to us the product or service that, in the opinion of AI, we need the most right now. On news or entertainment resources, AI selects and recommends to us the events and content that should be of the greatest interest to you and me. Or, after scrolling through a huge amount of texts, it gives us a text response to our query, similar to a human one. In relation to such recommendation systems, there is already a rule of law requiring the owner to disclose the algorithm of their operation. I want both users and Roskomnadzor to be able to verify that the results of such recommendation systems are harmless to people.
At the same time, AI should not destroy existing relationships in the digital ecosystem. Artificial intelligence extracts knowledge from the digital space in the same way that minerals are extracted. And for this "digital raw material", AI must "pay", be it financial resources or traffic, thereby ensuring the development and functioning of the information resources they use. Of course, there is a risk of monopoly dictate from the owners of such systems. Therefore, transparency of relationships and the introduction of effective systems of independent, objective measurement, such as the online advertising accounting system we have created, is extremely important.
We need to find an approach that will allow us to strengthen the links between digital services through AI and make them more effective for users. The final outlines of this model have not yet been determined, but it is necessary to actively engage in its formation and programming of its result. AI provides superpowers in working with information analysis and synthesis, so defining these approaches is important for the scientific and technological development of the country as a whole.
— And here we come to the topic of creating some kind of uniform code of ethics for all countries for the creation and use of systems with artificial intelligence technologies?
— You need to start with your country. The knowledge extracted by AI should not have a negative impact on our users. It is important that they meet high quality standards, that is, they are reliable, relevant and safe, as well as based on reliable and verified sources.
Both the information sources themselves and the owners of AI systems should be responsible for this. Once again, transparency, traceability of information and its origin are at the forefront of this approach. To achieve these goals, it is necessary to fully and comprehensively regulate AI at the level of federal legislation with a clear definition of the responsibilities of specific entities.
What are the requirements for AI developers? Labeling of products created using AI, mandatory verification of generated content for compliance with legislation before publication or response to the user — comprehensive work of the State Duma, relevant authorities and other authorized structures is necessary to form an exhaustive list of tools.
With a competent approach to regulation, we will be able to create a fundamentally new source of systemic knowledge that is logically, historically, and hierarchically interconnected. AI is the most powerful leap in quality in working with information. Such AI systems will determine the speed and effectiveness of the country's scientific and technological development. Those who have their own will be ahead of those who do not have them.
— Today, even elementary school students know that online AI services can easily provide ready-made answers to almost any textbook question.
— Our education system has to adapt to such technological developments — both schools, special education, and higher education. It is necessary to exclude the atrophy of critical thinking skills and independent analysis. Artificial intelligence should not hinder creative synthesis, not limit it, not replace it, but help it. These are challenges for the organization of the educational process. New methods, new knowledge and skills are needed from teachers and mentors themselves.
AI can impressively shift the pace of development along all axes forward, or it can stop, set us back, making us indifferent consumers of other people's meanings and technologies. And our task is to eliminate these risks by making the emerging new AI-based relationships fair and safe, strengthening our intellectual potential.
— For a service like Roskomnadzor to work, you need both people and structured processes. Have you somehow restructured your work with the team?
— We have more than 7 thousand employees, most of them work in the regions of the country. We had to start with the formation of a common culture in the department, including the subordinate enterprise. It was decided to radically restructure the collaboration, making the work of the entire structure seamless, setting up unified end-to-end processes and working with employee motivation. We introduced a system for evaluating management personnel, horizontal relationships, and other performance indicators, which allowed employees to reach a level of understanding of the importance of their own contribution to achieving the goals of Roskomnadzor, comparable to leading IT companies.
Roskomnadzor also includes one of the country's oldest services, the radio frequency Service. Our signalmen constantly, around the clock, every day ensure the uninterrupted operation of electronic equipment throughout the country. This includes mobile communications, satellite communications, radio, and television. This is an extremely responsible job of our professional staff at the highest level. As you know, the demand for them is also high.
It was important for us to create conditions for every employee to understand the relationship between the daily tasks performed and the goals of the department. We have implemented functional management and eliminated duplication. There are end-to-end processes with common regulations.
New highly professional structures have been created at the subordinate enterprise for several years. New divisions have been created — for security, organizational and personnel development; the work of the Information Technology department has been restructured. The company has become the center of Roskomnadzor's digital transformation, where all our key developments are concentrated. In fact, the company has become a project office and an IT integrator for us, which fully ensures the implementation of the growing number of tasks and powers of the department. On their technical side, I mean.
— I suppose it was necessary to significantly restructure the recruitment system and adjust the requirements for candidates?
- of course. Without a sufficient staff of highly qualified technical specialists — programmers, ML developers, information security specialists, data analysts - our projects would not have worked. We have high requirements for personnel — they must be engaged and responsible professionals. Knowledge in the field of IT, communications, technology, and information law was a challenge for us in the context of a shortage of personnel in these areas and high competition from IT companies and communications companies.
We have completely modernized our HR department and established close cooperation with relevant universities and colleges throughout Russia, inviting their graduates for internships and subsequent employment in our departments. If there is a desire among young people to gain experience, then we are always open, we also take high school students to practice on real tasks. The main motivation of the younger generation is solving interesting and ambitious tasks. In addition, the mentoring mechanism helps when experienced employees are interested, including financially, in attracting young staff.
Since the beginning of the special military operation, the need for our work has become more urgent, and people have begun to see our work not as an agency of restrictions, but as an effective mechanism for protecting their families, children, and society as a whole in the digital environment. The average age of our employees is 43, and they are energetic and interested in the world around them, who have already started a family, and they share our values, participate in charity and social life. For our employees, working in the department is definitely a conscious choice. Our employees are true patriots who sincerely love their country and their work to protect the citizens of the country...
* — the LGBT movement is recognized as extremist in Russia and banned
Переведено сервисом «Яндекс Переводчик»




































