- Статьи
- Science and technology
- Dusty job: spare parts for lunar equipment will be made directly on the Earth's satellite
Dusty job: spare parts for lunar equipment will be made directly on the Earth's satellite

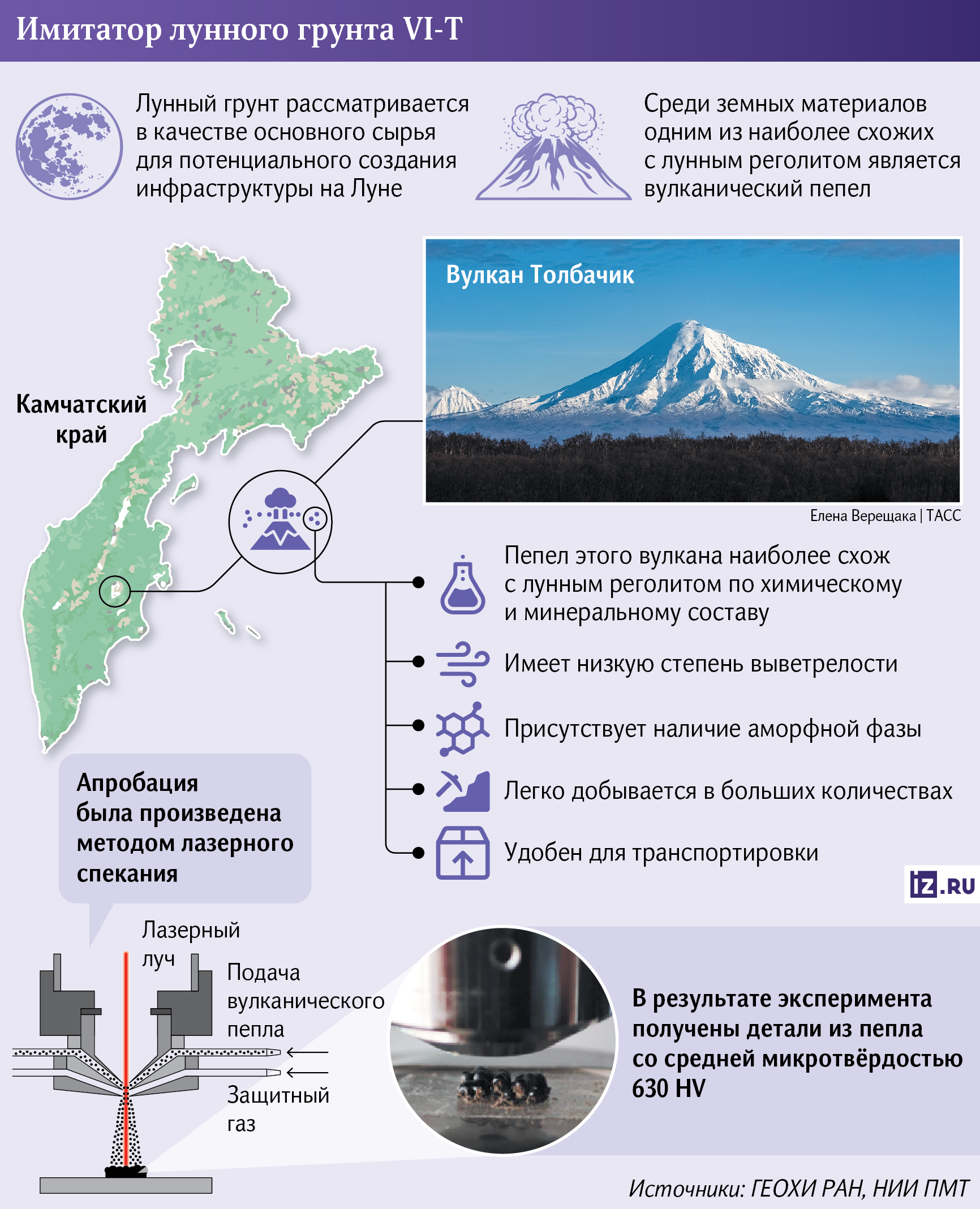
Russian scientists have developed and tested a technology for manufacturing small parts from lunar soil. The technique was tested on its terrestrial counterpart, which is made on the basis of ash and ash from the Tolbachik volcano. The proposed method involves laser sintering of particles. This method will make it possible to create the necessary spare parts for lunar technology directly on the satellite, which will significantly reduce the cost of space missions. Experts believe that the new technology will become in demand when a developed energy sector appears on the Moon.
How to get a lunar soil simulator
Russian scientists have tested the technology for manufacturing parts from an analog of lunar soil, which could be one of the key ways to create infrastructure directly on the Earth's satellite. This was reported in the press service of the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation. The staff of the Vernadsky Institute of Geochemistry and Analytical Chemistry (GEOHI) participated in the development RAS and the Scientific Research Institute of Advanced Materials and Technologies.
As the experts explained, the lunar soil simulator VI-T was used as the raw material. It is made from the ashes and ashes of the Tolbachik volcano, located in Kamchatka, for use in 3D printing technologies.
— Among terrestrial rocks, volcanic ash is the closest to the regolith (lunar soil) in terms of chemical and mineral compositions. At the same time, Tolbachik rocks have a low degree of weathering, they are easy to extract and they are convenient for transportation. The material is also characterized by the presence of an amorphous (non—crystalline) phase in it, which is not always present in other simulators," Ivan Agapkin, a junior researcher at the Laboratory of Geochemistry of the Moon and Planets of the GEOHI RAS, told Izvestia.
He explained that the soils on the surface of the Earth's satellite are divided into two types depending on their location. These are the dark rocks of the lunar "seas" and the light "mainland" rocks. However, in reality, the composition of the regolith is mixed in most areas. This is confirmed by the samples brought to Earth by the Apollo 11, Luna-16 and Chang'e-6 expeditions. Tolbachik's ashes correspond to this intermediate composition.
What spare parts for lunar vehicles can be created?
— The sample was produced by laser sintering, in which a powerful and thin beam of directional light fuses particles of the source material. As a result of the experiment, a sample measuring 5 mm by 15 mm with hardness characteristics sufficient for use in lunar conditions was obtained," said Ivan Agapkin.
According to him, the technology allows you to quickly create small products of complex shapes: screws, bolts, rings and other small-sized structures. However, the method is quite energy-intensive, so it will become fully in demand only at the stage when a developed energy industry appears on the Moon. For example, when a Russian nuclear-powered power plant is put into operation on its surface.
At first, more economical ways of processing the material will be developed on the Earth's satellite, the scientist suggested. For example, during the Chang'e-8 expedition, the technology of sintering regolith using concentrated solar radiation will be tested directly on the surface of the Moon. For these purposes, engineers have developed special devices that will focus light on areas of the lunar soil in order to melt it and bake it into solid bricks or slabs.
The Chang'e-8 station will go to the moon in 2028. Its goal is to develop technologies to create a future autonomous lunar research base.
How ground testing helps save money
— Testing equipment on the Ground helps to avoid risks and save significant resources. For example, earlier, when there was no understanding of what the lunar soil consists of, the designers did not know how to design landing modules — based on a soft or hard surface. This created a lot of uncertainties," said Alexey Karfidov, Head of the Department of Technological Equipment Engineering at MISIS University and General Director of the Karfidov Lab Design Bureau.
In general, laser processing together with 3D printing is a promising technology that opens up opportunities for creating new materials with improved properties, he added.
— The main advantage of laser sintering on the Moon is the ability to use local resources, which greatly reduces the cost of missions. The technology allows you to create high-strength structural elements and is easily amenable to automation. There is no atmosphere on the satellite that scatters laser beams. Therefore, the manufacturing accuracy of the parts will be higher," said Vyacheslav Belov, Associate Professor of the Department of Construction and Facilities of Thermal and Nuclear Power Engineering at the National Research University of Moscow State University.
However, the method has disadvantages: high energy consumption, complexity of the mechanisms and their sensitivity to lunar dust, temperature fluctuations and radiation, he added. A separate challenge is the preparation of regolith, so before application it is necessary to obtain fractions with a certain particle size.
— In addition to laser sintering, there are a number of other methods that are suitable for use in lunar conditions. The most basic is filling durable fabric bags with regolith and laying them by robots in the form of walls or horizontal surfaces. This method is simple and reliable, but the bags themselves need to be transported from the Ground," said Vladislav Florensky, a technician at the Laboratory for Research and Testing of Building Materials, Products and Structures at the Institute of Physics and Technology of the Russian Academy of Natural Sciences.
Mixing lunar soil with cement also requires less energy than sintering, but even in this case, the binder will have to be delivered from our planet. Another option is to build bases inside natural underground structures such as caves or lava tubes, the expert added. The disadvantages here are related to the need for complex exploration and reinforcement work.
— The surface of the moon is an aggressive environment. Therefore, when mastering it, it is necessary to build protection and life support systems. At the same time, the delivery of materials from Earth is extremely expensive. It is easier to bring the equipment and create the necessary facilities on the spot. This requires robots and additive technologies," explained Evgeny Dudorov, Director of the NGO Android Technology.
Before sending a man to the moon, it is necessary to work out technologies on Earth, the expert explained. According to him, this can be partially done using digital modeling, but practice shows that real conditions are much more complicated. Therefore, for the development of technologies, analogues of lunar materials are needed, which are similar in their physical and technical properties.
Переведено сервисом «Яндекс Переводчик»







